Throughout history, technological revolutions have often been driven by the relentless pursuit of connectivity—an innate human desire to bridge distances, share knowledge, and create communities beyond physical boundaries. At the core of this evolution lies wireless communication, which has transformed from rudimentary radio signals to the sophisticated, high-speed data transmission frameworks that underpin modern society. As the digital landscape continues to expand, network standards such as WiFi development symbolize our ongoing quest to dissect and enhance this connectivity fabric. Yet, beneath the technical jargon and industry buzzwords, there exists a fundamental philosophical inquiry: how does each new iteration of WiFi redefine our collective capacity for innovation, productivity, and social interaction? This article explores the broad, abstract principles of technological evolution in wireless networks, zeroing in on WiFi 7—a standard poised to reshape our digital experience—and examines its anticipated availability and implications within the grander scope of connectivity’s trajectory.
The Embodiment of Connectivity: From Basic Transmission to Seamless Experience

Humanity’s innate desire for connection manifests materially through the evolution of communication technologies. Each successor to the previous generation of Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) encapsulates a pursuit—not merely of faster speeds but of more seamless, ubiquitous, and reliable networks. At a philosophical level, this progression underscores the fundamental principle that technology serves as an extension of our consciousness—augmenting cognition, enabling new modes of collaboration, and reshaping societal structures.
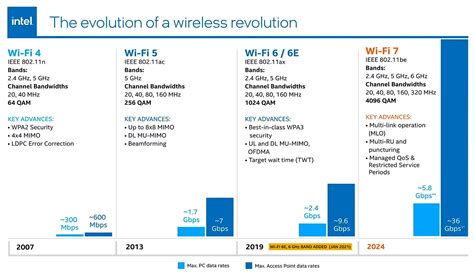
Early WiFi standards, such as 802.11b and 802.11g, prioritized basic wireless internet access, often constrained by limited frequency bands and modest data rates. Moving through the early 2000s, advancements like WiFi 4 (802.11n) and WiFi 5 (802.11ac) introduced multi-antenna technologies and wider bandwidths, subtly shifting the paradigm toward more stable, high-capacity transmissions. Now, with the advent of WiFi 6 (802.11ax), a new layer of complexity emerges—targeting not just speed but also quality of service, latency reduction, and energy efficiency. Each leap is a reflection of our philosophical drive to push the boundaries of proximity, presence, and immediacy in communication.
The Transition to WiFi 7: A Quantum Leap in Connectivity
WiFi 7, officially known as IEEE 802.11be, signifies a paradigm shift—a radical rethinking encapsulating the broader principles driving technological innovation. It aims to deliver theoretical maximum throughput of up to 30 Gbps, three times higher than WiFi 6, alongside reduced latency and enhanced reliability. This transition is not merely about raw data rates; it embodies a profound philosophical shift toward what can be described as “absolute connectivity”—where the digital and physical worlds increasingly converge.
Practically, WiFi 7 introduces advanced features such as 320 MHz channel bandwidths, multi-link operation (MLO), and 4096-QAM modulation, each representing a step forward in maximizing information flow within the network fabric. From the broader perspective, such advancements align with the concept of an interconnected society where everything—from autonomous vehicles to smart cities—is woven into a cohesive digital tapestry.
Release Timeline and Availability: When Will WiFi 7 Be on the Market?
Despite the remarkable technological potential of WiFi 7, a question persists among both industry experts and everyday consumers: when will the standard become widely available? Historically, the release of new WiFi standards follows a multistage process, including ratification by standards bodies, development of compatible hardware, and eventual commercial adoption. This sequence ensures technological robustness, interoperability, and user readiness.
Industry timelines reveal that the IEEE ratified the WiFi 7 standard in early 2023, paving the way for subsequent hardware developments. Following standardization, semiconductor manufacturers and networking device producers typically require approximately 12 to 18 months to deliver compatible routers, laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices. Consequently, the earliest consumer-grade WiFi 7 products are projected to reach the market by late 2024 or early 2025.
Moreover, the actual global deployment depends heavily on regulatory approvals, firmware updates, and market demand. Major technology companies, including Qualcomm, Broadcom, and TP-Link, have announced plans to release WiFi 7-compatible devices within this timeframe. These developments indicate that widespread adoption is likely to commence in earnest around 2025, with accelerated rollouts in industrial, enterprise, and smart city applications.
Industry Readiness and Consumer Accessibility
While technical specifications paint an optimistic picture of WiFi 7’s capabilities, practical accessibility remains contingent upon infrastructural investments and consumer awareness. Network providers and hardware vendors must integrate WiFi 7 into mainstream products, which involves overcoming challenges such as cost, backward compatibility, and network security considerations. The transition period, anticipated to span over 2-3 years, will be characterized by a gradual phasing-in of WiFi 7 standards within new routers, access points, and client devices.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Standard Ratification | IEEE 802.11be ratified in early 2023 |
| First Consumer Devices | Expected late 2024 to early 2025 |
| Mass Market Adoption | Projected around 2025-2026 |

Implications and Broader Significance of WiFi 7 Availability
The arrival of WiFi 7 signals a deeper philosophical transformation—moving toward an omnipresent digital environment where physical limitations give way to boundless informational flow. As connectivity reaches new heights, societal, economic, and personal paradigms are reshaped—fueling innovations, altering daily behaviors, and expanding human potential.
On a societal level, the increased bandwidth, reduced latency, and network robustness enable advancements in telemedicine, autonomous transportation, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). These technologies, inherently dependent on high-speed wireless networks, will thrive only when standards like WiFi 7 are fully operational, illustrating how technological evolution catalyzes broader cultural shifts.
Economically, the proliferation of WiFi 7-compatible devices fosters new markets and business models—ranging from smart cities and Industry 4.0 to immersive entertainment sectors. Yet, beneath these practical applications lies a more profound inquiry into digital equity: as connectivity becomes faster and more ubiquitous, how do we ensure equitable access for all segments of society? This challenge underscores the ongoing dialogue about technology as a democratizing force vs. a potential source of disparity.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, WiFi 7 also faces obstacles. Broad implementation requires significant infrastructural upgrades, mindful standard enforcement, and addressing security vulnerabilities inherent to high-speed, interconnected networks. Moreover, the transition phase may see compatibility issues, regulatory hurdles, and geopolitical considerations influencing international rollout timelines.
Additionally, concerns around data privacy and network resilience become more pressing as ultra-fast connectivity facilitates ever-increasing data transmission. It necessitates a balanced approach—advancing capabilities while maintaining safeguards—a challenge that remains central in the broader discourse on technological progress.
Key Points
- WiFi 7 introduces significant speed and efficiency upgrades with up to 30 Gbps throughput, enabling new technological frontiers.
- The standard’s first commercial deployment likely occurs between late 2024 and 2025, with widespread adoption by 2025-2026.
- Its emergence signifies a philosophical shift toward ubiquitous, high-fidelity connectivity that supports societal and economic innovation.
- Challenges remain in infrastructure, security, and equitable access as industries transition to this new wireless paradigm.
- Strategic early adoption offers competitive advantages for tech-forward organizations aiming to leverage ultra-low latency and massive bandwidths.
When is WiFi 7 expected to be available for consumers?
+The first WiFi 7-compatible devices are anticipated to launch between late 2024 and early 2025, with widespread market presence expected around 2025 or 2026, following infrastructure upgrades and manufacturer rollout schedules.
What makes WiFi 7 different from previous standards?
+WiFi 7 introduces multi-link operation, wider channels (up to 320 MHz), and higher-order modulation (4096-QAM), enabling speeds up to 30 Gbps, significantly lower latency, and more reliable multi-device connectivity, pushing the boundaries of wireless communication capabilities.
Will WiFi 7 be compatible with existing devices?
+WiFi 7 is designed to be backward compatible with previous WiFi standards, meaning newer routers will generally support older devices, but to leverage its full benefits, compatible hardware will be necessary. The ecosystem will evolve over several years to include both legacy and cutting-edge devices.



