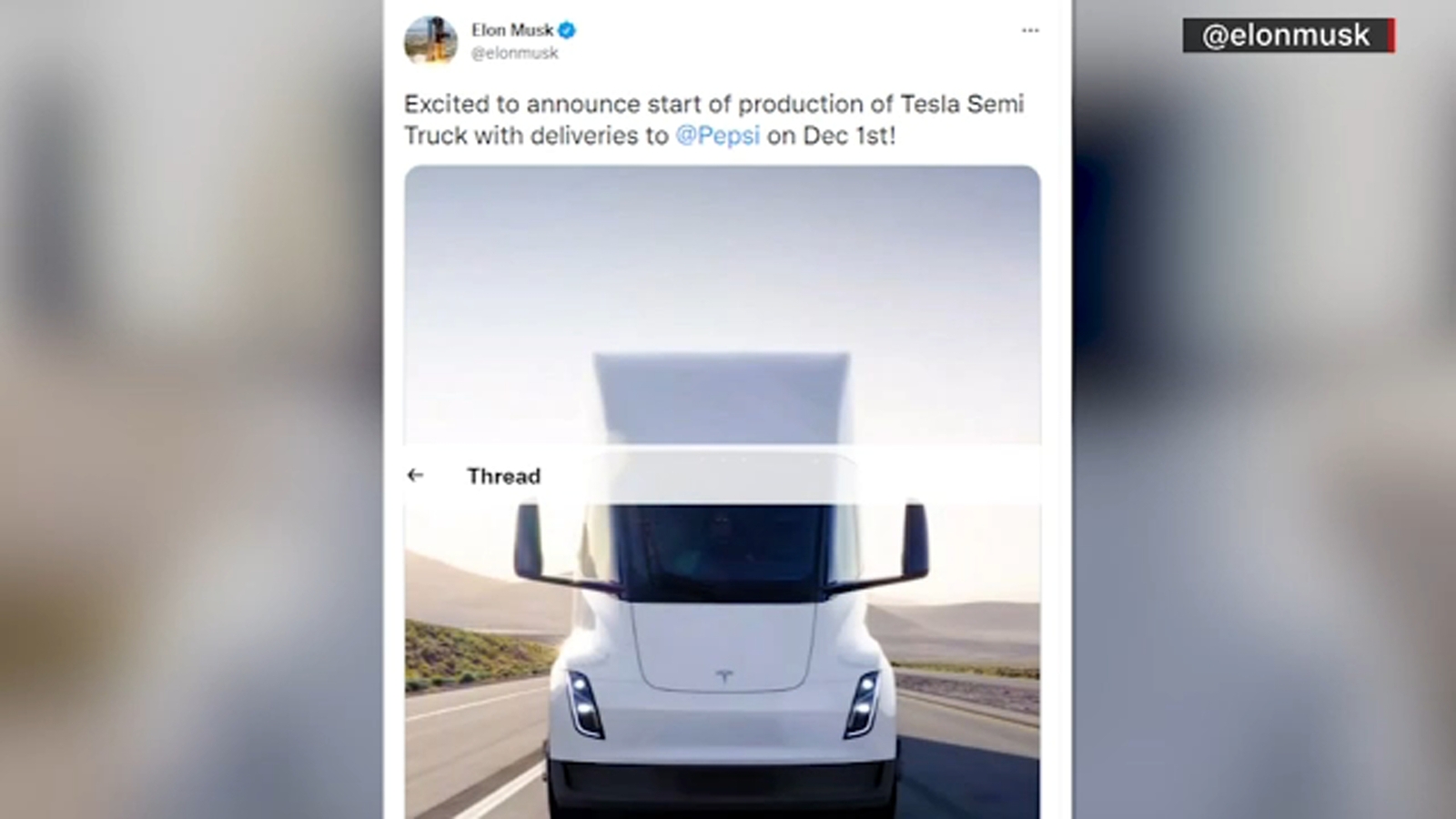
With the accelerating shift toward sustainable transportation, the electric commercial vehicle sector stands at a pivotal juncture, marked notably by Tesla's ambitious Semi truck project. As the industry, policy makers, and potential fleet operators watch keenly, the elusive release date of the Tesla Semi has become more than mere curiosity; it reflects broader technological, economic, and infrastructural transformations. Dissecting the pathways to uncover the Semi's official debut involves understanding the interrelated components of Tesla’s development timeline, regulatory environment, supply chain challenges, and strategic corporate disclosures—each influencing and being influenced by one another in a complex systems network.
Understanding Tesla Semi: An Overview within the Electric Vehicle Ecosystem

Launched amid significant anticipation, the Tesla Semi aims to revolutionize freight logistics by combining electric drivetrains with advanced autonomy capabilities. The Semi’s potential to cut operational costs, reduce emissions, and optimize fleet management makes its release date a critical datapoint not just for Tesla, but for the entire commercial electric vehicle industry. Such a launch triggers ripple effects across supply chains, infrastructure upgrades, and regulatory policies, positioning the Semi as a nexus point in sustainable transport systems.
The Evolutionary Timeline of Tesla’s Semi Development
Since its initial unveiling in November 2017, Tesla has articulated a long-term vision that extends beyond prototype demonstrations to mass production. Historically, Tesla’s product rollouts—such as the Model 3 and Model Y—show a pattern of delayed but ultimately successful launches, often influenced by technological hurdles, battery supply constraints, and manufacturing scaling challenges. The Semi’s development trajectory similarly hinges on advancements in battery cell density, thermal management systems, and self-driving hardware—each a technical subsystem whose maturation influences the overall release prospects.
| Key Milestones | Dates & Context |
|---|---|
| Announcement & Initial Reveal | November 2017, Las Vegas |
| First Prototype Drive | 2018-2019; Demonstration of range and acceleration capabilities |
| Production Delay Announcements | 2021-2023; Due to supply chain disruptions, chip shortages, and battery issues |
| Latest Strategic Updates | 2024; Tesla hints at upcoming production ramp-up and beta testing completion |

Decoding the Clues: How to Track Tesla Semi’s Official Launch

Due to Tesla’s characteristic secrecy around product timelines, enthusiasts and industry insiders employ a multifaceted approach to gauge the Semi’s release prospects. These include monitoring official filings, patent applications, supply chain disclosures, and public statements by Tesla’s leadership. Additionally, regulatory approvals—such as Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) certifications or Department of Transportation (DOT) filings—serve as concrete indicators of imminent production readiness. When combined, these dispersed signals form a systems-level picture hinting at the timing of the official release.
Official Communications and Corporate Disclosures
Tesla’s quarterly earnings reports and shareholder letters often contain subtle hints about product timelines. For instance, mentions of upcoming manufacturing milestones, factory capacity expansions at Gigafactories, or regulatory approvals for vehicle testing are key indicators. Tesla CEO Elon Musk’s Twitter updates also act as real-time pulse checks, although they require cautious interpretation due to their informal nature and occasional ambiguity.
| Disclosed Data Point | Implication for Release Date |
|---|---|
| Upcoming earnings call mentioning capacity increases | Potential ramp-up phase approaching, possibly indicating a near-term launch |
| Patent filings for battery and drivetrain innovations | Technological breakthroughs that could accelerate pilot production |
| Regulatory filings for heavy-duty vehicle testing | Imminent testing phase completion, possibly leading to certifications |
The Role of Regulatory Environment in Shaping Release Timelines
Regulators play a pivotal role in setting the legal and safety frameworks necessary for commercial deployment. The Tesla Semi, categorized as a Class 8 heavy-duty electric vehicle, must meet rigorous standards imposed by agencies like the EPA, DOT, and similar international bodies. The certification process typically involves comprehensive testing of emissions compliance, safety features, and autonomous driving systems. These interdependent elements function like a regulatory feedback loop—delays or advancements in one area ripple through the entire timeline, either delaying or hastening the official launch.
Certification Processes and Interdependencies
Achieving full regulatory certification involves multiple stages, including crash testing, emissions verification, and autonomous system validation. Each of these stages depends on preceding test results, technological readiness, and manufacturing quality controls. The complexity increases with autonomous driving systems, which require extensive real-world testing and legal compliance in different jurisdictions. The convergence of these processes often becomes the bottleneck or accelerator in the release schedule.
| Regulatory Milestones | Expected Impact on Launch |
|---|---|
| EPA emissions certification | Could signal readiness for commercial operation |
| FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards) approval | Necessary for road legality in the US, potentially indicating near-term launch |
| Autonomous vehicle testing permits | Demonstrate system maturity, influencing delivery timelines |
The Strategic Influence of Supply Chain and Production Capacity
Underlying Tesla’s Semi schedule are complex supply chain networks, sourcing lithium, cobalt, nickel, and advanced semiconductors that are vital for battery packs and autonomous hardware. Delays in securing these raw materials, or in manufacturing high-capacity batteries at scale, directly affect the expected timelines. Tesla’s vertical integration—highlighted by its Gigafactories—partially mitigates some supply issues but also introduces new dependencies and logistical challenges.
Battery Supply Chain Dynamics
Battery technology is at the heart of electric heavy-duty vehicles. Tesla’s recent investments in battery cell production, notably the 4680 form factor, are designed to enhance energy density and reduce costs. However, scaling production to meet Semi’s anticipated volume remains non-trivial, with the Global Battery Alliance reporting capacity gaps of approximately 1,200 GWh annually by 2030 to meet EV market demands. These supply constraints are central to the timing of Semi’s mass availability.
| Supply Chain Metric | Impact on Product Launch |
|---|---|
| Battery cell capacity at Giga Texas and Berlin | Determines the pace of Semi production ramp-up |
| Raw material procurement timelines | Potential delays if bottlenecks persist |
| Global semiconductor availability | Affects autonomous hardware integration timing |
Forecasting the Tesla Semi Release: A Systems Approach

Mapping these interconnected parts—regulatory progress, supply chain resilience, technological maturation, and corporate strategic communication—provides a holistic view of the Semi’s potential rollout timeline. While the exact date remains uncertain, current indicators suggest that a confluence of these factors could enable the Semi to debut commercially within the next 12 to 18 months. This estimation rests on the premise that ongoing advancements in battery production, regulatory approvals, and factory ramp-ups reach critical thresholds simultaneously.
Potential Scenarios and Their Significance
In a best-case scenario, rapid regulatory approvals, stabilized supply chains, and announced production targets could see Tesla unveiling the Semi by late 2024, with initial deliveries early in 2025. Conversely, unforeseen delays in autonomous system certification or raw material procurement might extend this timeline into 2026. Recognizing these positions allows stakeholders to align expectations, investments, and strategic planning accordingly.
| Scenario | Implication |
|---|---|
| Optimistic | Possible launch before end of 2024 with strong market reception |
| Moderate | Launch pushed into mid-2025, with gradual deployment phases |
| Pessimistic | Delays into 2026 due to regulatory or supply chain setbacks |
Key Points
- Multi-factor analysis: Leveraging signals from regulatory, technological, and supply chain domains enhances prediction accuracy.
- Systems thinking framework: Interdependencies between components determine the overall timeline.
- Strategic monitoring: Combining official disclosures, patent activity, and market signals provides actionable foresight.
- Adaptive expectations: Flexibility in planning accounts for unpredictable delays inherent in complex systems.
- Implication for stakeholders: Manufacturers, fleet operators, and investors benefit from nuanced understanding of these interconnected factors.
What are the main indicators that suggest the Tesla Semi is nearing release?
+Key indicators include recent regulatory filings, certifications, Tesla’s official statements about production milestones, patent activity related to batteries and autonomous tech, and supply chain developments. When multiple signals align, they point toward an imminent launch window.
How do supply chain constraints influence the Semi’s release schedule?
+Supply chain bottlenecks—especially in battery materials and semiconductors—limit production capacity and delay certification processes. Resolving these bottlenecks is essential for scaling up manufacturing and aligning with planned release dates.
What role does regulatory approval play in unveiling the Tesla Semi?
+Regulatory approval ensures safety and emissions compliance, which are prerequisites for vehicle registration and commercial operation. Progress in this area often directly signals that the vehicle is close to market readiness.