In an era characterized by rapid technological evolution and heightened interest in satellite-based internet solutions, Starlink has emerged as a transformative force reshaping connectivity paradigms worldwide. Developed by SpaceX, Starlink's ambitious project to deploy a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites aims to deliver high-speed, low-latency internet access to even the most remote regions. With its groundbreaking approach, recent developments around the anticipated stock release date and the investment prospects associated with Starlink have garnered significant attention from investors, analysts, and tech enthusiasts alike. This guide offers a detailed, step-by-step analysis of the latest insights, contextualizes the strategic implications, and provides a comprehensive outlook on the potential encapsulated within this nascent yet promising venture.
Understanding Starlink’s Market Position and Strategic Rollout

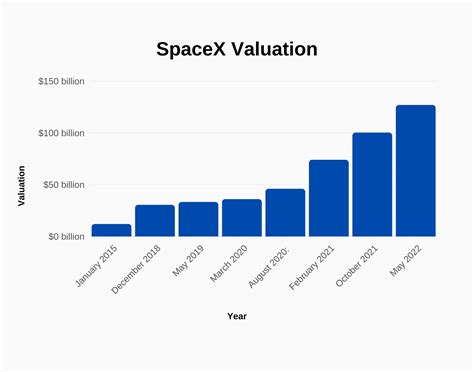
Starlink occupies a unique niche within the broader satellite communications industry. Unlike traditional geostationary satellite internet providers, its constellation of LEO satellites ensures more reliable, faster connections, which are particularly crucial in underserved and rural areas where terrestrial infrastructure is limited or nonexistent. This technological edge positions Starlink as a disruptive force with an expansive market opportunity estimated by industry analysts to reach over 4.8 billion potential users globally by 2030, representing substantial growth potential. Moreover, the strategic decision to transition the service to a publicly traded platform could unlock new avenues for capital infusion, facilitating accelerated satellite deployment and network expansion.
Key drivers influencing the stock release timeline
Multiple factors influence the timing of Starlink’s stock offering, including regulatory approvals, corporate restructuring, and market conditions. Notably, the ongoing \“authorization process\” across different jurisdictions remains complex, as authorities weigh the benefits against concerns over spectrum usage and space debris. Recent statements from SpaceX executives suggest a potential window within the next 12 to 18 months for the stock market debut, contingent upon successful regulatory navigation and internal corporate readiness. Additionally, market volatility driven by macroeconomic factors, such as inflation rates and geopolitical tensions, can accelerate or delay the timeline.
| Criterion | Latest Data & Context |
|---|---|
| Projected IPO Timeline | Next 12-18 months, subject to regulatory clearance |
| Typical Market Cap | Estimated between $50 billion to $150 billion upon listing |
| Satellite Deployment Status | Over 3,600 satellites launched, with further phases in development |
Assessing the Investment Potential of Starlink
Investors eyeing Starlink’s stock release are primarily interested in its growth prospects, technological dominance, and strategic positioning to capitalize on the expanding broadband market. The underlying technology boasts a latency of variable 20-30 milliseconds—comparable to fiber optic connections in urban settings—making it highly attractive in remote and developing markets. Furthermore, projected revenue streams from user subscriptions, enterprise solutions, and government contracts default to substantial for early adopters, with estimates suggesting revenues could approach $10 billion annually within five years of full operational deployment.
Revenue streams and financial forecasts
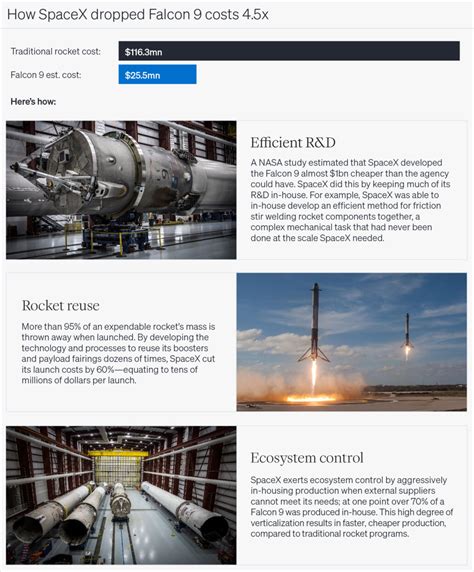
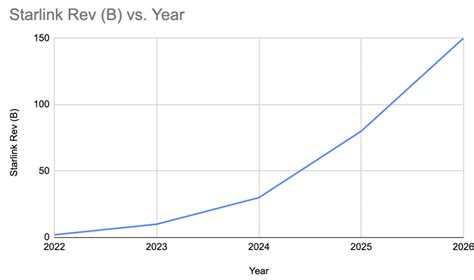
Starlink’s revenue model hinges on subscription fees, which currently range from 99 to 499 per month based on service tier and deployment region. Industry forecasts project a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of about 23% over the next decade, driven by global demand for reliable internet connectivity. The company’s ability to scale efficiently while maintaining low operational costs will be pivotal in translating revenue growth into sustained profitability. Furthermore, strategic diversification into enterprise, aviation, and maritime sectors broadens revenue bases, enhancing long-term financial resilience.
| Key Metric | Forecasted Data |
|---|---|
| Group Revenue (2024 projection) | $5-6 billion |
| Market Penetration Goal | To reach 20 million active users worldwide by 2028 |
| Cost per Satellite Launch | Approx. $60 million, with ongoing improvements reducing costs |
Potential Risks and Limitations for Investors
While Starlink’s prospects are compelling, prudent investors must weigh associated risks—including regulatory hurdles, space debris concerns, and technological uncertainties. Regulatory regimes vary significantly across nations, with some imposing strict licensing requirements that could either delay or limit market access. The space debris issue garners attention due to the potential for collision and the regulatory implications of congested orbital paths, which might lead to increased compliance costs or operational restrictions. Additionally, technological challenges such as satellite failure or interference can impact service quality, influencing investor confidence.
Mitigating risks: strategic considerations
Achieving a balanced outlook involves scrutinizing SpaceX’s capacity to navigate regulatory landscapes, manage satellite lifecycles effectively, and adapt to emergent industry standards. Diversification strategies, partnerships, and technological redundancies serve as risk mitigation avenues. For instance, adding ground infrastructure and terrestrial fiber links can complement satellite coverage, reducing reliance on space-based assets alone.
| Risk Factor | Impact & Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Regulatory delays | Potential postponements of IPO; managed through proactive compliance and lobbying |
| Space debris and congestion | Increased costs and operational restrictions; mitigated via satellite de-orbiting technologies |
| Technological failures | Service interruptions; addressed through redundancies and ongoing R&D |
Strategic Positioning and Long-Term Outlook
Starlink’s trajectory points to a grander vision—becoming the backbone of global internet coverage, especially aimed at facilitating digital inclusion and bridging the digital divide. Its success hinges on strategic evolution, including expanding coverage, optimizing satellite capacity, and forging strategic alliances with governments and corporate entities. The long-term outlook appears promising; as satellite technology matures, costs decline, and regulatory frameworks stabilize, the potential for mass-market adoption grows exponentially.
Evolutionary trends shaping satellite internet investments
Current trends emphasize miniaturization of satellites, increased lifecycle management, and the deployment of inter-satellite laser links for intra-constellation communication. These innovations promise to improve network latency and bandwidth, pushing Starlink and similar constellations toward near-terrestrial performance. Furthermore, the surge in demand for IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities amplifies the strategic importance of resilient connectivity, where Starlink’s infrastructure can serve as an enabler.
| Trend | Implication |
|---|---|
| Miniaturization of satellites | Lower launch costs and enhanced deployment flexibility |
| Inter-satellite laser links | Increased data transfer efficiency and network robustness |
| Integration with terrestrial networks | Enhanced coverage and reduced latency for end-users |
Conclusion: Decoding the Investment Potential and Strategic Timing
The anticipation surrounding Starlink’s stock release is a reflection of its groundbreaking technology, strategic scalability, and vast market potential. The projected timeline within the next 12 to 18 months appears manageable, yet contingent upon regulatory progress and internal corporate preparedness. For prospective investors, understanding the nuanced interplay between technological innovation, regulatory landscapes, and market dynamics is key to making informed decisions. While risks persist—ranging from regulatory delays to space debris management—the overarching potential of Starlink, positioned as a leader in satellite internet, is compelling. Its success could redefine internet accessibility globally, with substantial investment opportunities for those aligned with its strategic trajectory.
When is Starlink’s stock expected to be released?
+Current projections estimate a stock release within the next 12 to 18 months, depending on regulatory approvals and company readiness.
What are the main risks associated with investing in Starlink?
+Key risks include regulatory delays, space debris management challenges, technological failures, and market competition—each requiring strategic mitigation and ongoing management.
How does Starlink compare technologically with traditional internet providers?
+Starlink’s low Earth orbit satellite constellation offers significantly lower latency (20-30 ms) and broader coverage, especially in remote areas, which surpasses traditional geostationary satellites and many terrestrial options.
What long-term strategies should investors consider for satellite constellation companies?
+Focus on technological innovation, regulatory compliance, diversification of revenue streams, and strategic partnerships to sustain competitive edge and maximize growth potential over decades.