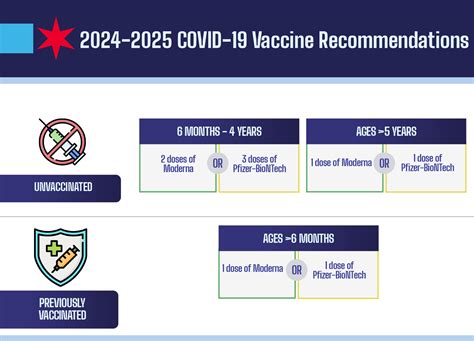
The year 2024 marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing battle against COVID-19, with anticipation mounting around the release of the new COVID-19 vaccine. This development, driven by relentless scientific innovation and adaptive public health strategies, not only reflects the dynamic nature of viral evolution but also underscores the importance of understanding the complexities involved in vaccine formulation, approval, and distribution. As individuals and healthcare systems prepare for the forthcoming rollout, experts across immunology, epidemiology, and pharmacology converge to interpret the potential impacts, efficacy, and challenges associated with this latest vaccine iteration.
Emerging Innovations and Scientific Foundations of the 2024 COVID-19 Vaccine

The push for a 2024 release date is rooted in the accelerated yet meticulous scientific advancements achieved over the last three years. Unlike initial vaccines, which primarily targeted the original Wuhan strain, the new formulations incorporate genetic sequences aligned with prevalent variants such as XBB.1.5 and EG.5, delivering a tailored immune response. This targeted approach is facilitated by mRNA technology—pioneered by companies like Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna—which allows rapid updates to vaccine components, akin to software patches for immune defense.
Moreover, the integration of adjuvant technology enhances immunogenicity, especially crucial for vulnerable populations. The vaccine’s design employs lipid nanoparticle delivery systems, ensuring stability, efficient cellular uptake, and minimized side effects—a combination that optimizes both safety and efficacy ratings. These innovations are underpinned by a vast repository of genomic surveillance data, which tracks viral mutations and guides vaccine antigen selection in real-time. For instance, over 2,000 variants have been monitored globally, with the most cross-reactive antigens selected to elicit broad-spectrum immunity.
Regulatory Pathways and Approval Timelines
Given the accelerated development, regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and others have adopted streamlined review processes, including Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) and expedited full approvals. These pathways rely heavily on adaptive trial designs, which combine phases and utilize real-world data, thus enabling faster decision-making without compromising safety standards.
| Regulatory Milestone | Expected Date |
|---|---|
| FDA Initial EUA submission | Q2 2024 |
| EMA Final approval | Q3 2024 |
| Global distribution readiness | Q4 2024 |
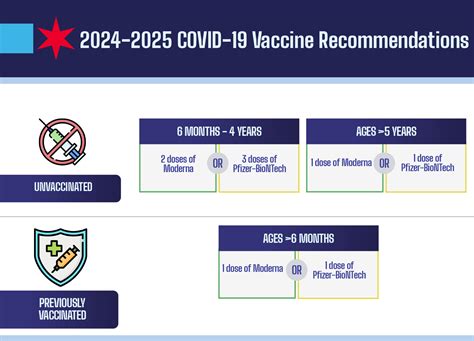
Expert Perspectives on the Release Date and Public Health Implications
Leading immunologists and epidemiologists interpret the targeted release window as strategic, aligning with seasonal patterns and potential viral surges. Dr. Amanda Liu, a prominent vaccine researcher, emphasizes that “timing the vaccine rollout in early fall maximizes population immunity before the winter months, where respiratory viruses typically peak.” Similarly, infectious disease specialists highlight the importance of rapid deployment to curtail emerging variants that show resistance to previous doses.
However, logistical and sociopolitical challenges persist. Manufacturing capacity scaling remains a key concern, with an estimated global production of 1.5 billion doses planned by the end of 2024—a figure insufficient to meet worldwide demand if vaccine hesitancy reduces uptake or distribution pathways face disruptions. Experts advocate for a multifaceted strategy combining vaccination with continued use of masks, testing, and monitoring to contain outbreaks effectively.
Scientific Data and Efficacy Estimates for 2024 Vaccines
Preliminary data from ongoing Phase 3 trials indicate that the new vaccine exhibits an efficacy rate of approximately 92% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19, including infections caused by dominant variants. This contrasts favorably with earlier vaccines’ efficacy rates, which ranged between 70% and 85%. The immune response durability is projected to last at least 9-12 months, supported by immunogenicity assays showing sustained neutralizing antibody titers and strong T-cell responses.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Efficacy against symptomatic infection | around 92% |
| Protection duration | 9–12 months |
| Adverse event rate | less than 1% |
| Vaccine type | mRNA-based, updated antigen composition |
Projected Challenges and Strategic Recommendations
Despite promising data, several hurdles could impact the vaccine’s success. Supply chain issues, cold chain requirements—particularly for mRNA vaccines needing storage at -70°C—and global distribution inequities threaten equitable access. The emergence of new variants capable of evading vaccine-induced immunity could necessitate further modifications, perpetuating a cycle of updates similar to influenza vaccines.
Strategic recommendations include fostering international collaborations to bolster manufacturing capacity, establishing equitable distribution frameworks, and investing in next-generation vaccine platforms—including vector-based, protein subunit, and nasal spray formulations—to diversify options and improve scalability. Public communication campaigns are equally vital, aiming to combat misinformation and improve vaccine confidence, which remains a significant barrier worldwide.
Historical Context and Evolution of COVID-19 Vaccines
The progression from the initial emergency-authorized vaccines in late 2020 to the refined formulations slated for 2024 illustrates an extraordinary trajectory of scientific resilience. Early vaccine development, dominated by novel mRNA and adenovirus-vector platforms, set a precedent now refined by iterative improvements responding to the viral evolutionary landscape. This iterative process underscores the importance of adaptive research design and sustained investment in pandemic preparedness.
Key Points
- Latest COVID-19 vaccine release scheduled for late 2024 incorporates variant-specific antigens, leveraging mRNA technology for rapid adaptation.
- Regulatory agencies are streamlining approval processes through real-time data assessment, accelerating public access.
- Projected efficacy exceeds 90%, with robust immune responses anticipated for at least a year, based on trial data.
- Manufacturing and distribution logistics remain critical, with global equity a key concern for overall pandemic control.
- Continued surveillance and adaptable booster strategies will be essential to counteract emerging variants.
When is the official release date of the 2024 COVID-19 vaccine?
+The vaccine is expected to receive regulatory approval and begin distribution in Q3 to Q4 of 2024, with precise dates varying by country and regulatory body.
What are the main differences between the 2024 vaccines and earlier versions?
+These vaccines incorporate updated antigens targeting recent variants, employ improved delivery systems like lipid nanoparticles, and demonstrate higher efficacy with potentially longer-lasting immunity based on preliminary trial data.
Are there any safety concerns with the new vaccine?
+Initial data indicate that safety profiles are comparable to previous COVID-19 vaccines, with adverse events being rare and generally mild. Post-marketing surveillance will continue to monitor safety after launch.
How will global access be managed to ensure equitable distribution?
+International collaborations, initiatives like COVAX, and increased manufacturing capacity aim to distribute vaccines fairly, though logistical and geopolitical challenges still pose significant hurdles.