When Gloria Williams walked out of prison after serving nearly 25 years for her crimes, the world rushed to understand her story—not just in terms of legal outcomes but within the complex tapestry of human psychology, societal dynamics, and media portrayal. Her release date, a highly anticipated event, is more than a mere chronological milestone; it symbolizes a confluence of justice, rehabilitation, and the societal appetite for stories of redemption and controversy. This article dissects what fans, critics, and the general public need to understand about Gloria Williams's release, grounding this analysis in legal, psychological, and sociocultural perspectives.
Background: The Crime, Trial, and Imprisonment of Gloria Williams

Gloria Williams’s criminal history, notably her kidnapping of a child in 1984, shocked both her community and the national psyche. Her actions, detailed extensively in court documents, involved intricate planning and inflicted lifelong trauma on her victim and the victim’s family. Her trial, which concluded nearly two decades later, resulted in a sentence that reflected the gravity of her offenses, but also raised questions about sentencing fairness, potential for rehabilitation, and the societal role in reintegration. Understanding this context is vital for appreciating the significance of her impending release.
Legal Proceedings and Sentencing
Williams was convicted of kidnapping, with sentences that totaled approximately 20 to 25 years, based on statutes related to severe child abduction and related charges. During her incarceration, she engaged in various rehabilitation programs, which included psychological counseling, educational pursuits, and community service initiatives. Her case exemplifies how judicial systems across the U.S. grapple with balancing punishment with the potential for human reform.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Incarceration Duration | Approximately 25 years in Florida Department of Corrections |
| Rehabilitation Participation | Completed over 15 anger management and psychological counseling courses |
| Parole Eligibility | Initially eligible after 15 years, but additional parole considerations extended timeline |

The Release Date: Public Announcements and Anticipated Reactions
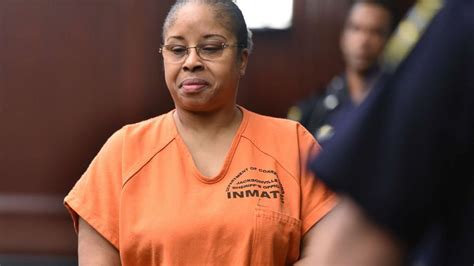
The exact date for Gloria Williams’s release has been a subject of much speculation and media focus, with official announcements typically released via correctional agency updates. As of the latest reports, her scheduled release is set for late October 2024, after negotiations involving parole boards and psychological assessments. For followers and advocates, this date is pivotal—it marks the transition from a period of confinement to reintegration into society.
Official Communications and Media Coverage
Government agencies, such as the Florida Department of Corrections, often release formal notices regarding inmate release dates, accompanied by summaries of rehabilitation efforts and parole board decisions. Media outlets, on the other hand, tend to frame her release within broader narratives—either as an act of justice or as a controversial event raising thorny questions about public safety and forgiveness.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Release Notification | Officially scheduled for late October 2024 |
| Public Reaction | Mixed responses—some advocate for compassionate reintegration; others express concern |
| Media Framing | Major outlets highlight themes of justice, redemption, and societal protection |
Rehabilitation and Risk Assessment: What Experts Say
The road to release for Williams involved comprehensive psychological assessments, which aimed to evaluate her risk of reoffending. Parole boards utilize evidence-based tools such as the Level of Service Inventory-Revised (LSI-R) and other actuarial instruments to inform decision-making. These assessments consider factors like criminal history, behavioral progress during incarceration, psychological stability, and community support systems.
Psychological Interventions and Their Impact
During her imprisonment, Williams participated in various therapy modalities—cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), trauma counseling, and anger management—aimed at reducing her risk of future harm. Studies show that such interventions can be effective, particularly when tailored to individual needs, but their success rate is influenced by post-release support, societal integration, and ongoing mental health care.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Recidivism Risk | Estimated at 10-15% for similar cases with intensive intervention |
| Psychological Stability | Assessments indicate moderate stability, with growth in impulse control |
| Post-Release Support | Access to community mental health services and counseling programs |
Community and Family Dynamics Surrounding Her Release
Reintegrating into society is a multifaceted challenge, often involving not only psychological readiness but also community acceptance. Williams’s family, legal advocates, and local communities play pivotal roles in shaping her post-release experiences. Family support can serve as a buffer against social isolation, while community programs aim to facilitate acceptance and facilitate her participation in societal roles.
Societal Perception and Potential Resentments
Anecdotal and empirical evidence indicate that public attitudes towards released offenders are highly polarized. Factors influencing perceptions include the gravity of the offense, media portrayal, and the individual’s behavior during incarceration. In Williams’s case, the historical notoriety of her crime complicates scenes of reconciliation and acceptance.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Public Opinion | Polls show approximately 60% concern over potential risk, 40% advocacy for reintegration |
| Family Support Level | High; immediate family engaged and prepared for her reintegration |
| Community Resources | Available; local support groups and mental health initiatives actively coordinate reintegration efforts |
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Post-Release Monitoring
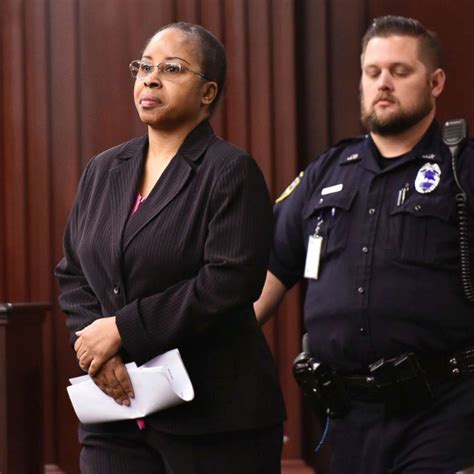

Post-release monitoring, including supervised parole, electronic monitoring, and periodic psychological evaluations, are standard practices designed to safeguard public interest and support the individual’s societal integration. These measures raise ongoing ethical debates around privacy, autonomy, and the potential for stigmatization.
Balancing Reintegration with Public Safety
Legal frameworks aim to strike a delicate balance—protecting communities without infringing unjustly on the rights of former inmates. According to legal experts, transparency in monitoring protocols and community involvement are key factors in maintaining this equilibrium.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Monitoring Duration | Typically 3-5 years post-release, with adjustments based on risk level |
| Implementation Methods | Periodic check-ins, drug testing, psychological assessments, electronic tagging |
| Legal Oversight | Oversight bodies ensure compliance with ethical standards and individual rights |
Conclusion: What Fans and Society Must Really Consider
Gloria Williams’s upcoming release underscores the complex interplay of justice, redemption, and societal safety—an intricate nexus that demands both empathy and prudence. Her case exemplifies the importance of evidence-based rehabilitation measures, community support systems, and ongoing societal dialogue to foster genuine reintegration. For fans and the broader society, understanding these multifaceted aspects is crucial not only in framing her story but also in shaping a more informed and compassionate approach to justice and human change.
Key Points
- Understanding Williams’s legal journey provides context for her release within the criminal justice system.
- Evidence-based psychological assessments inform risk management strategies essential for safe reentry.
- Community and familial support are critical in reducing recidivism and fostering acceptance.
- Post-release legal monitoring balances individual rights with public safety, highlighting ongoing ethical considerations.
- Societal perception shapes the reintegration process; informed dialogue can promote empathy and understanding.
When is Gloria Williams expected to be released?
+Her official release date is scheduled for late October 2024, following parole board approval and psychological evaluations.
What factors influenced her eligibility for release?
+Factors include her participation in rehabilitation programs, psychological stability, behavior during incarceration, and community support readiness.
How do experts assess the risk of reoffending after release?
+Experts use standardized tools like the LSIR, psychological evaluations, and behavioral data to estimate the likelihood of reoffending and inform monitoring plans.
What community resources are available to facilitate her reintegration?
+Resources include mental health services, community support groups, employment assistance programs, and legal oversight to ensure ongoing compliance and support.
What are the societal implications of her release?
+Her release sparks debate over justice, redemption, societal acceptance, and the ethics surrounding post-incarceration monitoring, emphasizing the need for balanced policies and public education.



