Every month, millions of investors, economists, policymakers, and financial professionals eagerly anticipate the release of the Consumer Price Index (CPI), a key indicator that shapes monetary policy and influences everyday economic decisions. The CPI is not just a number; it embodies a complex interplay of data collection, statistical methodology, historical context, and systemic timing, all woven into a precise schedule that balances accuracy with timely reporting. Understanding the timeline behind CPI release dates is essential for comprehending how inflation metrics are constructed, how they impact markets, and how transparency in economic reporting is maintained. This guide takes a deep dive into the intricate process, revealing the story behind each scheduled release, the steps involved, and how these dates can influence decision-making across various sectors.
Understanding the Importance of CPI and Its Release Schedule
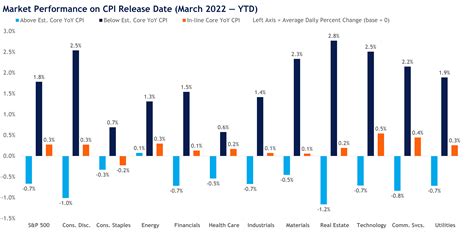
The Consumer Price Index measures the average change over time in the prices paid by consumers for a market basket of goods and services. As a primary inflation indicator, the CPI influences monetary policy decisions, wage negotiations, and indexation of social benefits and pensions. Because of its high stake, the timing of its release is meticulously planned and communicated well in advance to maintain market credibility and data integrity.
Across different jurisdictions—most notably in the United States from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), and in other economies through their national statistical agencies—the release schedule is rooted in established protocols that reflect both operational capacity and the need for comprehensive, verified data. Recognizing these timelines helps stakeholders prepare, react, and interpret CPI movements with confidence, ultimately anchoring economic stability and guiding policy interventions.
Key Points
- Core scheduling strategies ensure CPI releases are timely and reliable, balancing data accuracy with market needs.
- Understanding the timeline enhances anticipatory analysis, allowing investors and policymakers to better interpret inflation trends.
- Systematic planning incorporates various procedural steps, from data collection to final publication, often spanning several weeks.
- Communication protocols guarantee transparency and prevent market surprises that could destabilize financial markets.
- Historical context and procedural evolution illustrate how CPI dissemination has adapted to technological advancements and data complexity.
The Standard CPI Release Cycle: Sequence and Timing
Most national statistical agencies follow a structured cycle for CPI releases, typically synchronized on monthly or quarterly schedules. For example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) adheres to a predictable timetable that is publicly documented well in advance, facilitating strategic planning across sectors.
Step 1: Data Collection and Preliminary Processing
The process begins approximately two to three weeks before the scheduled release. During this phase, data collectors gather prices across retail outlets, service providers, and online sources. This process involves rigorous field surveys, scanner data from retailers, and administrative records. The collected data undergo initial validation, cleaning, and adjustment to account for seasonal variations or anomalies.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Data Collection Duration | Approximately 15-20 days before release |

Step 2: Data Analysis and Index Aggregation
Following collection, statisticians analyze the raw data, adjusting for seasonality, quality changes, and new product introductions. The core objective is to produce a representative, weighted index reflecting the consumer experience. This phase typically lasts about a week, culminating in the calculation of individual item price movements, which then feed into the aggregate CPI.
Step 3: Quality Assurance and Validation
Before publication, the CPI undergoes multiple validation steps, including cross-checks with auxiliary datasets, internal reviews, and external audits. Agencies often have multiple review boards that verify methodological consistency and data integrity. This process may add an additional week, ensuring that the final figures are robust and credible.
Step 4: Schedule Finalization and Pre-Announcement Briefings
Once validated, the statistical agency confirms the official release date, often issuing advance notices to market participants and media outlets. This transparent communication is a pillar of trust, allowing stakeholders to prepare for the release and immediate analysis.
| Relevant Metric | Lead time between final validation and release |
|---|---|
| Typically | 0-3 days before scheduled publication |
Step 5: Publication and Dissemination
The CPI data are published at a designated time, often early in the morning to maximize transparency and access. The release includes summary tables, detailed methodological notes, and contemporaneous commentary explaining the key movements observed. Additional dissemination channels, such as press releases, online dashboards, and live briefings, ensure broad accessibility.
Factors Influencing CPI Release Dates and Variability
While most agencies strive for consistency, numerous factors can influence the precise timing of CPI release dates:
Operational Constraints and Data Processing Demands
Delays in data collection, technological failures, or resource limitations can cause shifts. For instance, sudden surges in retail prices or supply chain disruptions (as seen during global events like pandemics) may prolong validation processes, prompting schedule adjustments.
Policy and Political Considerations
In some economies, political pressures or strategic timing—such as coinciding with fiscal reports or economic policy announcements—may influence release dates to optimize media attention or policy impact.
Technological and Methodological Changes
Implementation of new statistical methodologies, such as chained indices or quality adjustment techniques, may necessitate interim schedules or phased releases to manage transition complexities.
Historical Evolution: From Manual to Digital and Real-time CPI
The CPI’s release timeline has undergone significant change over decades. Initially, manual collection of prices involved extensive field surveys, and reports appeared weeks after data collection. Today, electronic scanning of receipts, online price databases, and real-time tracking enable much faster processing, with some agencies releasing preliminary indices within days of data collection completion.
This evolution enhances responsiveness but introduces challenges—such as maintaining methodological consistency and data security—which agencies address through protocol upgrades and transparency initiatives.
Case Study: The U.S. CPI Schedule
The BLS operates on a predictable schedule: data collection spans approximately 30 days, with final validation happening within the subsequent 10-day window. The CPI report is then generally released on the second or third Tuesday of each month at 8:30 a.m. Eastern Time. This schedule provides market participants with a reliable calendar, essential for planning and analysis.
| Important Date | Action |
|---|---|
| 15th-20th of month | Data collection completion |
| 21st-31st of month | Data analysis and validation |
| First Tuesday of month | Official CPI release |
Impact of CPI Release Dates on Markets and Public Policy

Knowing the precise timing of CPI releases can be a strategic advantage. Market analysts often position their trades ahead of scheduled announcements, tightening their focus around these dates to interpret the data’s potential market-moving impact. Central bankers, too, consider these schedules when calibrating monetary policy, especially if inflation trends deviate unexpectedly from forecasts.
Furthermore, scheduled CPI releases influence media coverage, corporate wage negotiations, and social benefit adjustments. Clear timing allows the public and institutions to prepare and respond accordingly, reducing informational asymmetries and fostering transparency.
Best Practices for Stakeholders in Anticipation of CPI Releases
- Maintain awareness of official calendars published by statistical agencies and economic calendars maintained by financial data providers.
- Prepare analytical frameworks that incorporate potential CPI movements, especially during periods of economic volatility.
- Establish contingency plans to adapt to schedule shifts or irregularities caused by operational or external factors.
- Engage with methodological disclosures to understand how seasonal adjustments and quality changes influence CPI figures.
- Foster transparency and communication with data providers and policymakers for early insights or clarification.
Conclusion: The Symphony of Timed Data and Market Stability
The timeline behind CPI release dates is a finely tuned system, balancing technological advancements, methodological rigor, operational capacity, and transparency. Recognizing the stages—from initial data collection through validation to publication—offers invaluable insight into the inner workings of inflation measurement. For investors, policymakers, and consumers alike, understanding this story enhances the ability to interpret economic signals, anticipate market moves, and comprehend the broader narrative of how economic health is communicated to the world.
How predictable are the CPI release dates?
+In most countries, official release dates are published well in advance and follow a consistent monthly schedule, making them highly predictable for stakeholders.
What causes delays in CPI release schedules?
+Delays can result from data collection issues, technological problems, extraordinary events like supply chain disruptions, or methodological updates that require additional validation time.
How has technology changed CPI release timelines?
+Advancements such as electronic data capture, big data analytics, and automation have shortened the processing cycle, enabling near real-time releases in some jurisdictions.
Why is the CPI release schedule important for markets?
+Markets often position themselves strategically around CPI release dates, as the inflation data significantly influences monetary policy, interest rates, and investor sentiment.
Can the release date ever be changed due to external factors?
+Yes, unforeseen circumstances such as natural disasters, political decisions, or systemic failures can prompt agencies to adjust scheduled release dates to ensure data validity and integrity.



