The anticipation surrounding high-performance computing processors reaches its zenith with recent revelations about the 9900x3d release date. As the industry continues its relentless pursuit of computational excellence, understanding the strategic positioning, technical advancements, and market implications of this forthcoming release becomes crucial for both enthusiasts and enterprise users. This article endeavors to dissect the multifaceted aspects of the 9900x3d launch, comparing it to existing flagship processors, analyzing technological innovations, and predicting its impact on computational paradigms.
Comparative Analysis of the 9900x3d and Established High-End Processors

To contextualize the significance of the 9900x3d, it is essential to juxtapose it against current industry titans such as AMD’s Ryzen 9 7950X3D and Intel’s Core i9-13900K. The focal points of this comparison include architectural improvements, core and thread count, thermal design power (TDP), and performance benchmarks across diverse computational tasks. While AMD’s 7950X3D has pioneered the 3D V-Cache technology to enhance gaming and specific workloads, Intel’s i9-13900K offers a hybrid architecture emphasizing multi-threaded processing capabilities. The 9900x3d, expected to integrate cutting-edge 3D stacking technology and optimized node manufacturing, aims to redefine high-performance benchmarks.
Architectural Innovations and Technological Underpinnings
The upcoming 9900x3d is rumored to utilize an advanced 3D stacking fabrication process, possibly leveraging TSMC’s 3DFabric or equivalent-established methods. This technique could enable stacking high-density cache layers directly atop the core complex, significantly reducing latency and increasing cache size—integral attributes for gaming, scientific computing, and AI workloads. Additionally, meticulous process node advancements—potentially transitioning to Intel 4 or TSMC 3nm equivalents—promise lower power consumption and higher frequency ceilings, setting new industry standards.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
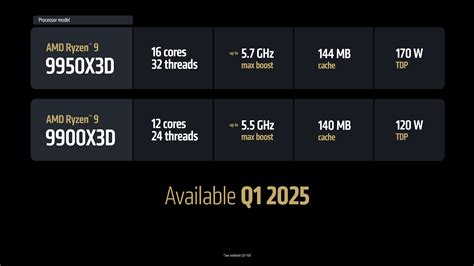
| Expected Launch Date | Q4 2024, with official announcements likely at CES 2025 |
| Core Count | Potentially 24 cores / 48 threads—an increase over previous models |
| Cache Size | Estimated 512MB to 1GB of L3 cache, incorporating 3D V-Cache technology |
| Manufacturing Node | Likely utilizing TSMC 3nm or Intel 4 process technology |
| Power Efficiency | Projected TDP of around 250W, with efficiency gains from process innovations |
Key Points
- Revolutionized Cache Architecture: Potentially doubling cache sizes through 3D stacking for reduced latency.
- Process Node Advancement: Leveraging cutting-edge nanofabrication to enhance performance and efficiency.
- Market Positioning: Aiming to outperform current leaders in both gaming and compute-intensive tasks.
- Strategic Launch Timing: Scheduled for Q4 2024, with significant industry implications.
- Potential Challenges: Power consumption and thermal management at high core counts remain critical considerations.
Comparing Architectural Directions: Vertical Stacking vs. Hybrid Architectures

One of the most defining features of emerging high-end CPUs like the 9900x3d is the emphasis on vertical stacking technologies, notably involving 3D V-Cache and other advanced packaging solutions. In contrast, traditional architectures such as Intel’s hybrid design with performance cores (P-cores) and efficiency cores (E-cores) exemplify a divergent evolutionary approach aimed at balancing raw power and power efficiency. Analyzing these strategies sheds light on the trajectory of processor development and their respective advantages.
Vertical Stacking: Amplifying Cache with 3D Technologies
Vertical stacking involves placing multiple layers of silicon die atop one another, interconnected through through-silicon vias (TSVs). This approach dramatically increases cache capacity without enlarging the physical footprint of the silicon die. Applications benefiting most from such innovations include gaming, high-frequency trading, neural network inference and other latency-sensitive tasks. Nonetheless, challenges such as heat dissipation, manufacturing complexity, and cost escalation are significant hurdles for mass adoption.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Major Benefit | Significantly increased cache with reduced latency, boosting performance in cache-dependent workloads |
| Limitations | Higher manufacturing costs and heat management complexities |
Hybrid Architecture: Balancing Power and Performance
Conversely, hybrid architectures like Intel’s Alder Lake or upcoming Raptor Lake components utilize a combination of high-performance cores and low-power cores to optimize workloads dynamically. This approach emphasizes power efficiency and workload adaptability rather than sheer peak performance. The advantages are clear: lower power consumption, better multitasking, and scalable performance in portable devices. However, this diversification sometimes results in increased complexity for software optimization and system design.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Performance Focus | Optimized for overall efficiency and multitasking across diverse workloads |
| Drawbacks | Complexity in workload scheduling and potential performance ceiling in single-threaded scenarios |
Implications for the Market and Ecosystem Readiness
The impending release of the 9900x3d will undoubtedly influence supply chains, software ecosystems, and industry standards. Hardware acceleration through increased cache and advanced process nodes invites a re-evaluation of existing architectures utilized in data centers, gaming, AI inference, and scientific research. Compatibility with existing motherboard chipsets and memory standards will be deciding factors in its adoption rate.
Market Positioning and Competitive Edge
Producers such as Intel and AMD have driven the high-end processor market through aggressive innovation cycles and strategic partnerships. The 9900x3d aims to carve out a substantial share by offering superior cache sizes, higher core counts, and better thermal efficiency, potentially rendering earlier generations obsolescent. Nonetheless, market penetration depends heavily on production scalability, manufacturing costs, and ecosystem support.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Expected Market Impact | Disruption across gaming, HPC, AI sectors; potential to shift upgrade cycles and procurement strategies |
| Compatibility Concerns | Motherboard BIOS updates, memory support, and thermal management solutions are essential for seamless adoption |
Conclusion
The 9900x3d release, scheduled for late 2024, encapsulates the latest in processor innovation—integrating advanced 3D stacking cache technology, cutting-edge process nodes, and a balanced architectural approach. By contrasting it with traditional hybrid architectures and emphasizing the potential of vertical stacking, this analysis illuminates a clear trend toward maximizing cache efficiency and thermal performance. As industry stakeholders prepare for its debut, the real-world impact remains dependent on manufacturing scalability, market acceptance, and software ecosystem readiness. For enthusiasts, professionals, and industry analysts alike, the 9900x3d stands as a testament to the relentless drive toward computational supremacy, promising to unlock new frontiers in processing power.



