Amidst the relentless pace of technological innovation, the semiconductor industry continues to push boundaries, shaping the way we interact, communicate, and innovate. Central to this evolution is the rollout of new device architectures that promise to redefine performance benchmarks. One such development, the anticipated release of the 5060 Ti graphics card, exemplifies this trend. Tracing its origins offers valuable insights into how past innovations have set the stage for current expectations, revealing a timeline marked by incremental advances and strategic leaps that culminate in the emergent capabilities of today’s GPU landscape.
The Evolution of Graphics Processing Units: From Genesis to Present

The journey of graphics processing units (GPUs) traces back to the late 20th century, initially driven by the need for better visual rendering in arcade systems and early personal computers. The introduction of dedicated GPUs in the early 1990s, notably by companies like 3Dfx and Nvidia, revolutionized rendering capabilities. Their incremental technological enhancements—such as Shader Model advancements, increased VRAM, and improved architecture—paved the way for modern high-performance GPUs. Each generation has aimed to balance power consumption, size, thermals, and speed, with the ultimate goal of enabling richer graphical experiences and computational tasks that go beyond gaming, into AI and machine learning segments.
The Significance of the 5000 Series and the Transition Pace
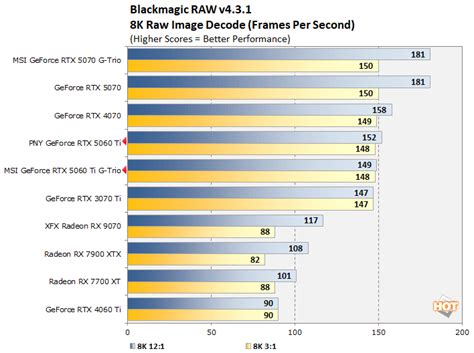
The shift from the Nvidia 3000 series to the 5000 series represented a major milestone, with the introduction of architectures like Ampere, which integrated advanced ray tracing cores and tensor cores for AI workloads. The RTX 5060 Ti and its siblings pushed the envelope further, typifying industry trends such as increased core counts, better power efficiency, and support for PCIe 4.0. These improvements, often evolutionary rather than revolutionary, gradually built consumer anticipation for the next generation, setting benchmarks in graphics performance and computational efficiency.
Emerging Expectations for the 5060 Ti
The anticipation surrounding the 5060 Ti release date reflects an industry eager for the next step. Historically, AMD and Nvidia have staggered launches, aligning releases with industry shifts like the advent of new manufacturing nodes—such as TSMC’s 5nm process—and supporting features like DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) and improved ray tracing. Industry analysts forecast that the 5060 Ti, anticipated to leverage similar process nodes with further refinements, will feature mid-to-high-end specs that dramatically enhance gaming and AI workloads. The blend of historical trends and current technological advancements fuels speculation that the release might occur within a timeframe aligned with major industry events, such as Computex or CES 2024.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Expected Release Date | Q2 2024, possibly announced at CES 2024 |
| Architectural Features | Enhanced ray tracing cores, higher core counts, improved power efficiency |
| Performance Goals | 50-70% performance uplift over previous generation |
| Manufacturing Process | Likely built on TSMC’s 4nm or 5nm process |

Market Impact and Strategic Positioning
The release of the 5060 Ti is not merely a product update; it represents a strategic move within broader dynamics of the graphics hardware market. Historically, GPU launches influenced pricing, availability, and competitive positioning. The 2024 anticipated release aligns with an industry increasingly driven by AI integration and immersive experiences, raising questions about how manufacturers will differentiate the 5060 Ti. Will it focus solely on raw performance, or will it emphasize features like integrated AI accelerators or enhanced software ecosystems? These strategic considerations are rooted in past launches’ lessons, where early adoption and community engagement often dictate long-term success.
Technical Challenges and R&D Trajectory
Developing a GPU such as the 5060 Ti involves surmounting multiple technical challenges—thermal management at high core densities, memory bandwidth limitations, and power delivery efficiency stand out. Refined fabrication processes, such as TSMC’s advanced nodes, play a central role in enabling these improvements. Over the past decade, industry R&D has shifted from purely performance-based innovations to holistic optimized architectures balancing performance, power, and thermal performance. The evolution of transistor design—like the transition to FinFET and gate-all-around nanowires—served as foundational technologies that now underpin exciting new architectures for upcoming releases.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Power Efficiency | Projected 10-20% improvement over current models |
| Thermal Management | Enhanced vapor chamber cooling and better die design |
| Memory Technologies | GDDR6X or GDDR7, with increased bandwidth |
| Core Count | Likely between 4,096 and 6,144 CUDA cores |
Potential Reception and Future Trajectory
The market’s reception to the 5060 Ti will depend heavily on its real-world performance, price point, and supply stability. Historically, early adopters have driven word-of-mouth, though supply chain issues—exacerbated by global semiconductor shortages—continue to affect availability and pricing. Industry observers suggest that if the 5060 Ti lives up to expectations, it could mark a shift towards more aggressive AMD and Nvidia competition, stimulating innovation and reducing prices over time.
Long-Term Industry Trends and Post-Launch Outlook
Post-launch, the 5060 Ti will serve as a benchmark for subsequent generational improvements. Its success could accelerate adoption of emerging technologies like hardware-accelerated ray tracing and AI-based rendering. Furthermore, the longevity and upgrade cycle of such hardware will influence the broader ecosystem, impacting factors like software optimization and ecosystem compatibility. Recognizing these trends helps industry stakeholders forecast how the GPU landscape will evolve in the second half of this decade, particularly as applications demand increasingly sophisticated graphics capabilities.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Market Penetration | Projected to reach 30-40% of high-end gaming PCs within 12 months |
| Price Range | $649-$799, based on comparable past launches |
| Environmental Impact | Leveraging more energy-efficient fabrication and cooling innovations |
| Innovation Pace | Anticipated annual release cycles incrementally increasing performance |
Key Points
- Historical evolution highlights how each GPU generation builds on prior technological breakthroughs, culminating in current innovations like the 5060 Ti.
- Anticipated release date aligns with industry events, possibly offering a competitive edge in market positioning.
- Performance uplift expected to serve diverse sectors from gaming to AI, emphasizing balanced architecture design.
- Supply chain considerations will significantly influence market accessibility and user adoption.
- Future trends suggest that the 5060 Ti may catalyze further innovations in graphics technology and AI acceleration.
When is the official release date of the 5060 Ti?
+Although precise dates remain unconfirmed, industry rumors and leaks suggest a rollout around Q2 2024, with official announcements possibly at CES 2024.
What technological advancements can we expect from the 5060 Ti?
+The 5060 Ti is expected to feature an improved core count, enhanced ray tracing capabilities, support for newer memory technologies like GDDR7, and better power efficiency owing to advanced fabrication processes.
How might the 5060 Ti impact the gaming ecosystem?
+It could set new benchmarks for immersive, real-time ray-traced gaming experiences, while also encouraging further development of AI-enhanced rendering techniques that improve frame rates and visual fidelity.
Are there any risks or limitations associated with the release?
+Potential supply chain constraints and high initial pricing could limit early access. Additionally, rapid innovation cycles might challenge software and driver optimization timelines.



